Introduction
Odoo’s modular architecture is one of the main reasons for its flexibility and popularity. A crucial feature that makes this modularity possible is inheritance. Inheritance in Odoo allows developers to customize and extend existing models and views without altering the core codebase, ensuring upgradability and clean code management.
In my blog, I shall explore two major types of inheritance in Odoo 17:
- Model Inheritance: Reusing or extending data models
- View Inheritance: Modifying user interfaces dynamically
Model Inheritance
In Odoo supports three types of model inheritance:
| Type | Use case | Technical detail |
| Classical | Create a new model based on an existing one | Uses _name and _inherit |
| Extension | Add/modify fields in an existing model | Uses _inherit only |
| Delegation | Use another model’s fields through a relation | Uses _inherits and M2O field |
Let’s look at each specific area in detail.
1.Classical Inheritance
This method allows you to create a new model that inherits all fields and methods from another model. You use both _name and _inherit.
Use Case: When you want to build a new model that is structurally similar to an existing one, but with its own identity.
Example:
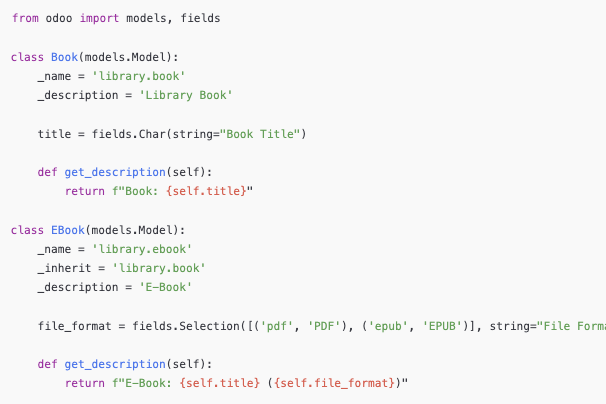
The library.ebook model inherits all fields and methods from library.book, but it also adds a new field (file_format) and overrides the method.
2.Extension Inheritance
In this case, you’re not creating a new model — you are extending an existing model by adding or modifying fields or methods. You only define _inherit.
Use Case: When you want to add features to existing models (e.g., add new fields to res.partner, product.template, etc.)
Example

Now all partner records (res.partner) will have a new field and method without altering the original core model.
3.Delegation Inheritance
This type of inheritance uses the _inherits attribute and is based on composition, not class-style inheritance. You define a many2one field linking to another model and delegate access to its fields.
Use Case: When you want to use another model field without merging into the same table.
Example:

The library.book model inherits fields like name and nationality from library.author via the author_id field, while keeping their data in separate tables.
View Inheritance
Odoo views are defined using XML. View inheritance allows you to extend existing UI views — you don’t need to override the whole view; just define what you want to insert, change, or remove.
Use Case: Add fields, buttons, or tabs to a standard Odoo form or tree view.

These have some key attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
| inherit_id | Reference to the original (parent) view |
| xpath | XPath selector to target a specific XML node |
| position | Where to insert/modify content: before, after, inside, replace |
| arch | XML structure containing the changes |
Alternative Syntax
Sometimes, you can use an alternative simplified structure:

Both formats are valid; use whichever gives you better control depending on the structure of the parent’s view.
Final thoughts
Inheritance in Odoo 17 is designed to empower developers to write modular, scalable, and upgrade-safe code. Once you understand when to use each inheritance strategy, you can customize virtually any part of Odoo without ever touching the core modules.
Whether you’re adding a custom field to a form view, extending a core model, or creating a new model that is built on existing logic — whatever your project, then you should reach out to my colleagues at zen8labs – we are the team that will help you to create something awesome.
Duong Phi, Software Engineer